In the world of cryptocurrencies, understanding the mechanics behind transactions is crucial for both new and experienced users. A crypto wallet serves as a digital vault for your assets, and one of its key functionalities is the ability to sign transactions securely. But what happens after a crypto wallet signs a signature? This article delves into the steps that follow this critical process, helping you grasp the underlying technology and enhancing your knowledge of blockchain transactions. Understanding these processes can empower you to engage more confidently with cryptocurrencies and ensure wallet security.
Understanding Digital Signatures
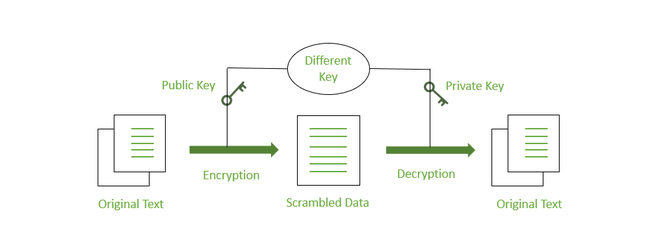
Digital signatures are cryptographic proofs that verify the authenticity and integrity of digital messages or documents. In the context of blockchain technology, they serve as a crucial element in securing crypto transactions. When a user initiates a transaction, the wallet generates a unique digital signature using their private key. This signature acts as a personalized identifier, ensuring that only the rightful owner of the wallet can authorize the transaction.
The private key is a confidential piece of data that must be kept secure, while the public key is shared with the network to facilitate transaction verification. Together, they form the basis of secure communication in the blockchain, where the digital signature can be validated by anyone with access to the corresponding public key, thus ensuring trust and transparency in crypto transactions.
The Signing Process
Understanding the signing process is essential for grasping how crypto transactions function. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
Initiating the Transaction
The process begins when a user wants to send cryptocurrency to another wallet. The user inputs the recipient’s wallet address, the amount to be sent, and any additional data required for the transaction.
Signing with the Private Key
Once the transaction details are set, the wallet uses the user’s private key to sign the transaction. This key is kept secret and is crucial for proving ownership of the funds.
Creating the Digital Signature
After signing with the private key, a unique digital signature is generated. This signature acts like a cryptographic fingerprint that authenticates the transaction, ensuring that it hasn’t been tampered with and confirming that the sender has authorized the transaction.
What Happens After Signing?
Transaction Broadcast
Once a crypto wallet signs a transaction, the signed transaction is broadcasted to the network. This involves sending the transaction data to multiple nodes within the blockchain network. Nodes are crucial as they serve as the backbone of the network, responsible for receiving, validating, and propagating transactions. Each node independently checks the validity of the transaction based on the cryptographic signature and ensures that it conforms to the network’s rules before forwarding it further.
Verification by Miners/Validators

After the transaction is broadcast, it reaches miners or validators, who play a pivotal role in maintaining the blockchain’s integrity. They verify the signature using the sender’s public key, confirming that the transaction was indeed authorized by the wallet holder. This step is critical because it prevents unauthorized transactions and ensures the security of the network.
The verification process is further strengthened by consensus mechanisms, which are protocols that ensure all nodes agree on the validity of transactions before they are added to the blockchain. Common consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), each having its own method for validating transactions. These mechanisms not only help in confirming the legitimacy of transactions but also contribute to the overall security and reliability of the blockchain network.
Adding to the Blockchain
Once a crypto transaction is signed, it enters a crucial phase where it must be added to the blockchain. This process involves broadcasting the signed transaction to the network, where nodes—computers that maintain a copy of the blockchain—receive and validate it.
Miners or validators then confirm the transaction, checking the digital signature for authenticity and ensuring that the sender has sufficient funds. Once validated, the transaction is bundled with others into a block. This block is subsequently added to the blockchain, achieving immutability, meaning the transaction is permanently recorded and cannot be altered. This layer of security enhances the trustworthiness of blockchain technology and ensures the integrity of the transaction.
Transaction Finality
Transaction finality in blockchain refers to the point at which a transaction can no longer be reversed or altered. Once a transaction is included in a block and confirmed by the network, it is considered final. This concept is crucial as it provides assurance to users that their transactions are secure and irreversible.
The impact of transaction finality on user confidence is significant. Knowing that a transaction is permanent enhances trust in the system, encouraging more users to engage in crypto transactions. Additionally, it contributes to overall wallet security, as users can be assured that their funds are safely transferred without the risk of reversal.
Common Misconceptions
When it comes to crypto wallets and their signatures, several myths can create confusion among users. One common misconception is that signing a transaction grants access to the wallet’s private keys. In reality, the signature only proves ownership of the funds and authorizes the transaction without revealing sensitive information.
Another frequent concern is about the irreversibility of transactions. Once a transaction is signed and broadcasted to the network, it cannot be reversed. This emphasizes the importance of double-checking transaction details before signing, as errors can lead to irreversible loss.
Best Practices for Wallet Security

Ensuring the security of your crypto wallet is paramount, especially before and after signing transactions. Here are some essential tips:
- Use Reputable Wallets: Always opt for wallets from well-known providers with positive reviews. Research their security features, such as two-factor authentication and encryption.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): This extra layer of security helps protect your wallet from unauthorized access, even if your password is compromised.
- Keep Software Updated: Regular updates often contain security patches that protect against vulnerabilities. Always use the latest version of your wallet software.
- Backup Your Wallet: Regularly create backups of your wallet and store them in secure locations. This ensures you can recover your assets in case of a device failure or loss.
- Be Cautious with Public Wi-Fi: Avoid accessing your wallet or making transactions over public networks, as they can expose you to potential hacks.
- Use Hardware Wallets for Large Holdings: For significant amounts of cryptocurrency, consider using hardware wallets, which store your keys offline and are less susceptible to online threats.
- Educate Yourself on Phishing Scams: Be wary of unsolicited communications and always verify the authenticity of links before clicking. Scammers often create fake websites to steal your information.
By following these best practices, you can significantly enhance your wallet security and enjoy peace of mind while engaging in crypto transactions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wallet signatures play a crucial role in the security and integrity of crypto transactions. By understanding what happens after a crypto wallet signs a signature, users can gain confidence in their ability to manage and secure their digital assets effectively. This knowledge not only enhances your understanding of blockchain technology but also empowers you to navigate the complexities of cryptocurrency dealings with greater assurance. Stay informed about the transaction process to protect your investments and ensure wallet security.











